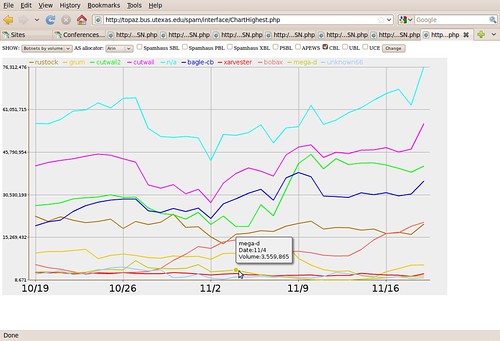
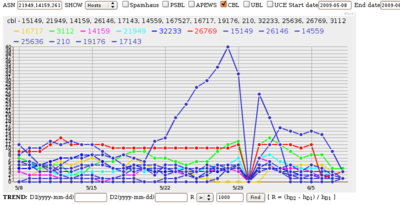
Good show! What effects did it have on spam? Not just spam from this botnet; spam in general.
This graph was presented at NANOG 48, Austin, TX, 24 Feb 2010, in FireEye’s Ozdok Botnet Takedown In Spam Blocklists and Volume Observed by IIAR Project, CREC, UT Austin. John S. Quarterman, Quarterman Creations, Prof. Andrew Whinston, PI CREC, UT Austin. That was a snapshot of an ongoing project, Incentives, Insurance and Audited Reputation: An Economic Approach to Controlling Spam (IIAR).
That presentation was enough to demonstrate the main point: takedowns are good, but we need a lot more of them and a lot more coordinated if we are to make a real dent in spam.
The IIAR project will keep drilling down in the data and building up models. One goal is to build a reputation system to show how effective takedowns and other anti-spam measures are, on which ASNs.
Thanks especially to CBL and to Team Cymru for very useful data, and to FireEye for a successful takedown.
We’re all ears for further takedowns to examine.
-jsq