Brian Krebs wrote on his blog,
Naming & Shaming Sources of Spam:
 A new resource for spotlighting organizations that are unwittingly
contributing to the global spam problem aims to shame junk email havens
into taking more aggressive security measures.
A new resource for spotlighting organizations that are unwittingly
contributing to the global spam problem aims to shame junk email havens
into taking more aggressive security measures.
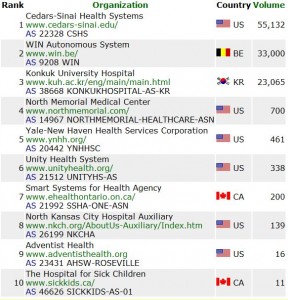
SpamRankings.net
is a project launched by the Center for Research in
Electronic Commerce at the University of Texas at Austin. Its goal is
to identify and call attention to organizations with networks that have
been infiltrated by spammers.
Andrew Whinston, the center’s director, said the group initially
is focusing on health care providers that appear to be infected with
spam bots. “Nobody wants to do business with a bank or hospital or
Internet hosting company that has been hijacked by spammers,” Whinston
said. “It’s an environment in which user data can be stolen or
compromised.”
The rest of his writeup quotes me quite a bit, and everyone knows I’m quite shy,
so please
go read his blog!
I will add that May data is live now on
SpamRankings.net.
Also, organizations that do better over time may want to brag,
as has happened with a couple of U.S. organizations in May.
Here’s Krebs’ final paragraph:
I applaud this effort, and hope that it gains traction. I remain convinced
that the Internet community would benefit from a more comprehensive and
centralized approach to measuring badness on the Web. There are many
existing efforts to measure reputation and to quantify badness online,
but most of those projects seek to enumerate very specific threats (such
spam or hacked Web sites) and measure the problem from a limited vantage
point. What is lacking is an organization that attempts to collate data
collected by these disparate efforts and to publish that information in
near real-time.
-jsq
Knock one down, two more pop up: Whack-a-mole is fun, but not a solution. Need many more takedowns, oor many more organizations playing. How do we get orgs to do that? …





